BACHD rats overexpress full-length human mutant HTT (mHTT) with 97 alternating CAA/CAG repeats on a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC).
The most important characteristics of BACHD rats are:
- mHTT aggregates
Quantification of polyQ HTT was performed using a sandwich immunosorbent assay by MesoScale Discovery. One transgenic BACHD rat was analyzed for polyQ HTT showing increased polyQ HTT levels compared to wild type rats. A dilution series of whole brain lysate of one rat was measured (Fig. 1).
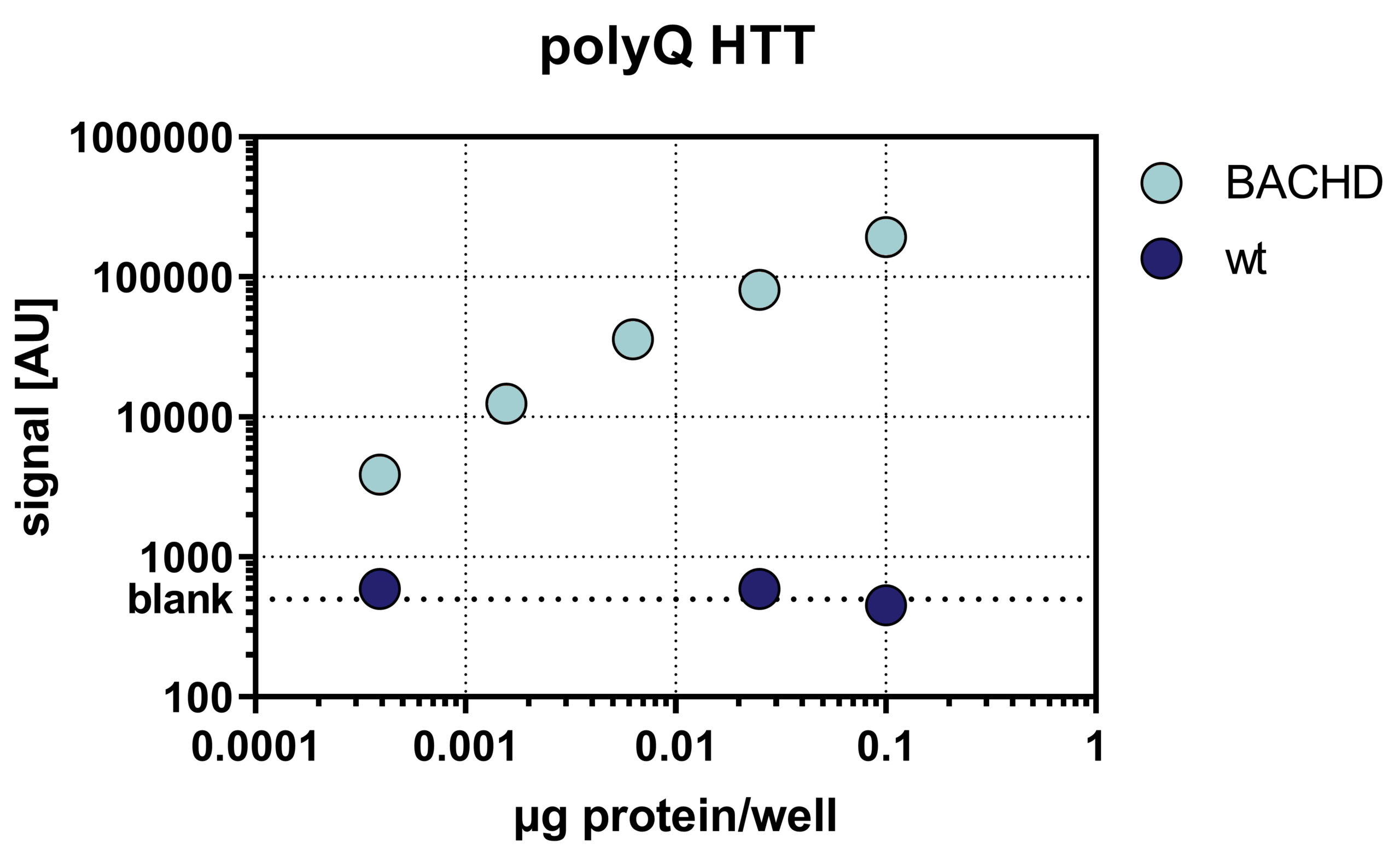
Figure 1: Quantification of polyQ HTT by sandwich immunosorbent assay using the MesoScale Discovery platform. Whole brain lysate of a 6 months old hemizygous rat and a non-transgenic littermate were used in a dilution series of 1:10, 1: 40; 1:160; 1:640 and 1:2560.
Scantox offers a custom-tailored study design for BACHD rats, and we are flexible to accommodate your special interests. We are also happy to advise you and propose study designs. Non-transgenic littermates are available as control animals needed for proper study design.
Scantox is ready to provide samples (brain tissue, CSF etc.) from these animals for analyses in your laboratory.
We are happy to evaluate the efficacy of your compound in the BACHD rat model! The most common readouts are:
Looking for something else? Please contact us!
