New Research Targets Tau Protein Abnormalities
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), and corticobasal degeneration (CBD) are all neurodegenerative diseases with one thing in common: abnormalities in tau, a key structural protein in the brain. Now, researchers at UC Santa Barbara may have discovered a way to interrupt the formation of neurofibrillary tangles that are made of misfolded tau protein. …
Impact of Tau Protein on Parkinson’s Disease Progression
As many as 10 million people worldwide are estimated to be living with Parkinson’s disease, a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement control. As the global population ages, Parkinson’s disease remains a significant public health concern, making ongoing medical research an urgent priority. Now, a new study published in the journal Brain may shed light on the progression of Parkinson’s disease, …
Could Pesticides Lead to Parkinson’s Disease?
Neurological disorders are now the leading source of disability around the world. Within that category, Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the fastest-growing neurological disorder, impacting more than 8.5 million people globally. Researchers have identified a number of environmental factors that contribute to the disease’s unprecedented rise — and the evidence is increasingly pointing to pesticides. Unfortunately, despite the growing body …
Is mRNA the Key to Treating Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) impacts as many as 500,000 Americans, though some estimates put that number as high as 1 million. There is currently no cure for PD, which means that healthcare providers are constantly on the lookout for effective therapeutic treatments to improve patients’ quality of life. Now, researchers at the Scripps Research Institute have developed a new …
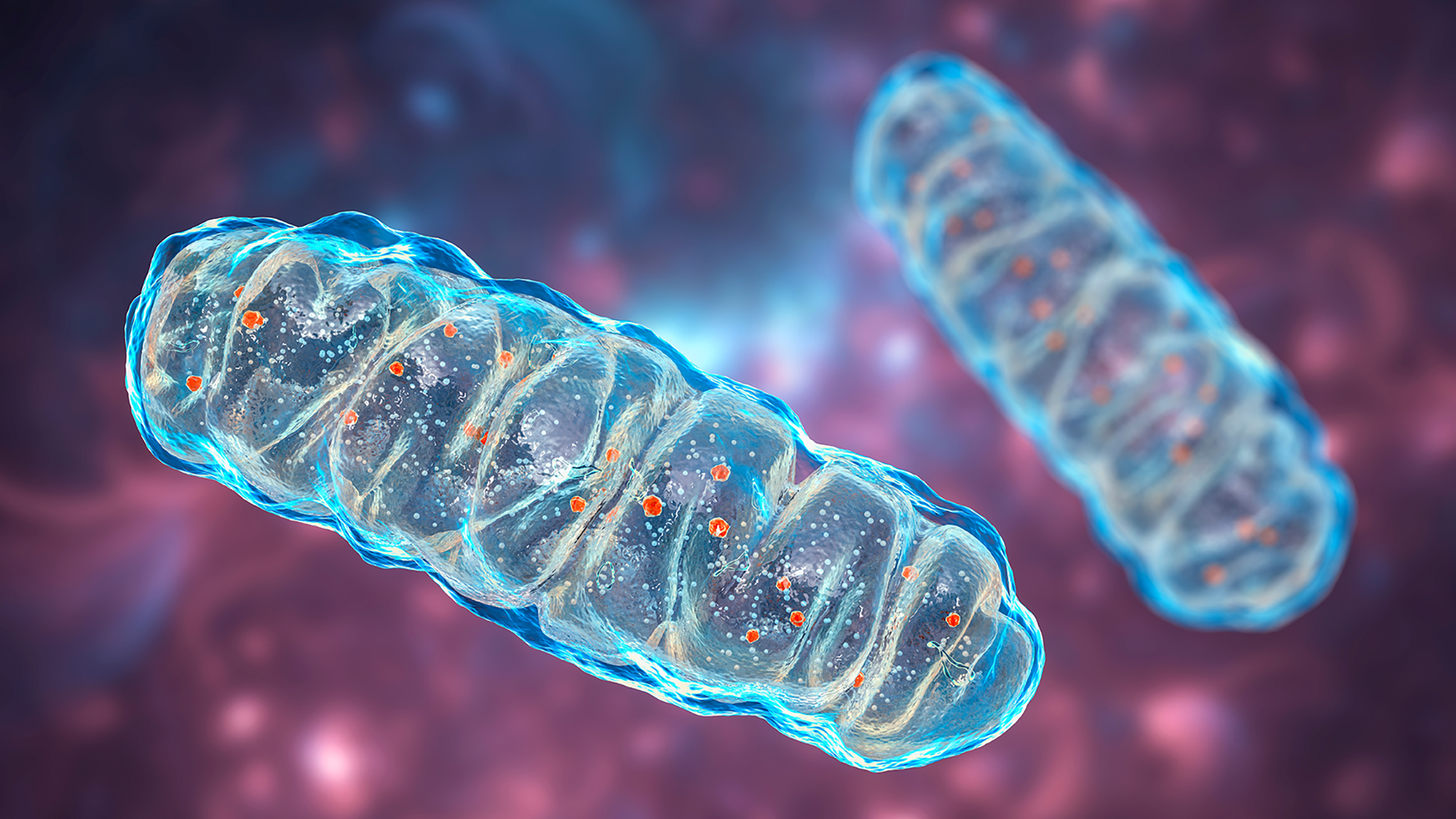
Could Malfunctioning Mitochondria Predict Alzheimer’s Disease?
Alzheimer’s Disease, or AD, is an incurable neurodegenerative condition that generally appears in individuals over the age of 65. However, scientists now believe that certain predictors can appear in a patient’s brain decades before symptoms appear — specifically, malfunctioning mitochondria. With that in mind, researchers at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) recently posed an …