Growth factor withdrawal assays have emerged as valuable tools to study neurological conditions associated with apoptosis. Neuronal cultures, depending on subtypes, rely on the substitution of multiple growth factors to maintain viability and health.
B27 is a widely used neuronal culture supplement that contains essential growth factors and nutrients supporting neuronal survival and function. By removing B27 from the culture medium of primary cortical neurons, the effects of growth factor deprivation in certain neurological conditions, like neurodegenerative diseases, ischemic injuries, developmental disorders, neuronal aging and neuroinflammatory conditions, can be mimicked.
Growth factor withdrawal assays allow for the examination of growth factor deprivation effects such as neuronal viability, morphology, functionality, and signaling pathways involved in multiple neurological conditions.
B27 withdrawal reduces cell viability in cortical mouse neurons (Fig. 1). The effect can be reversed through treatment with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
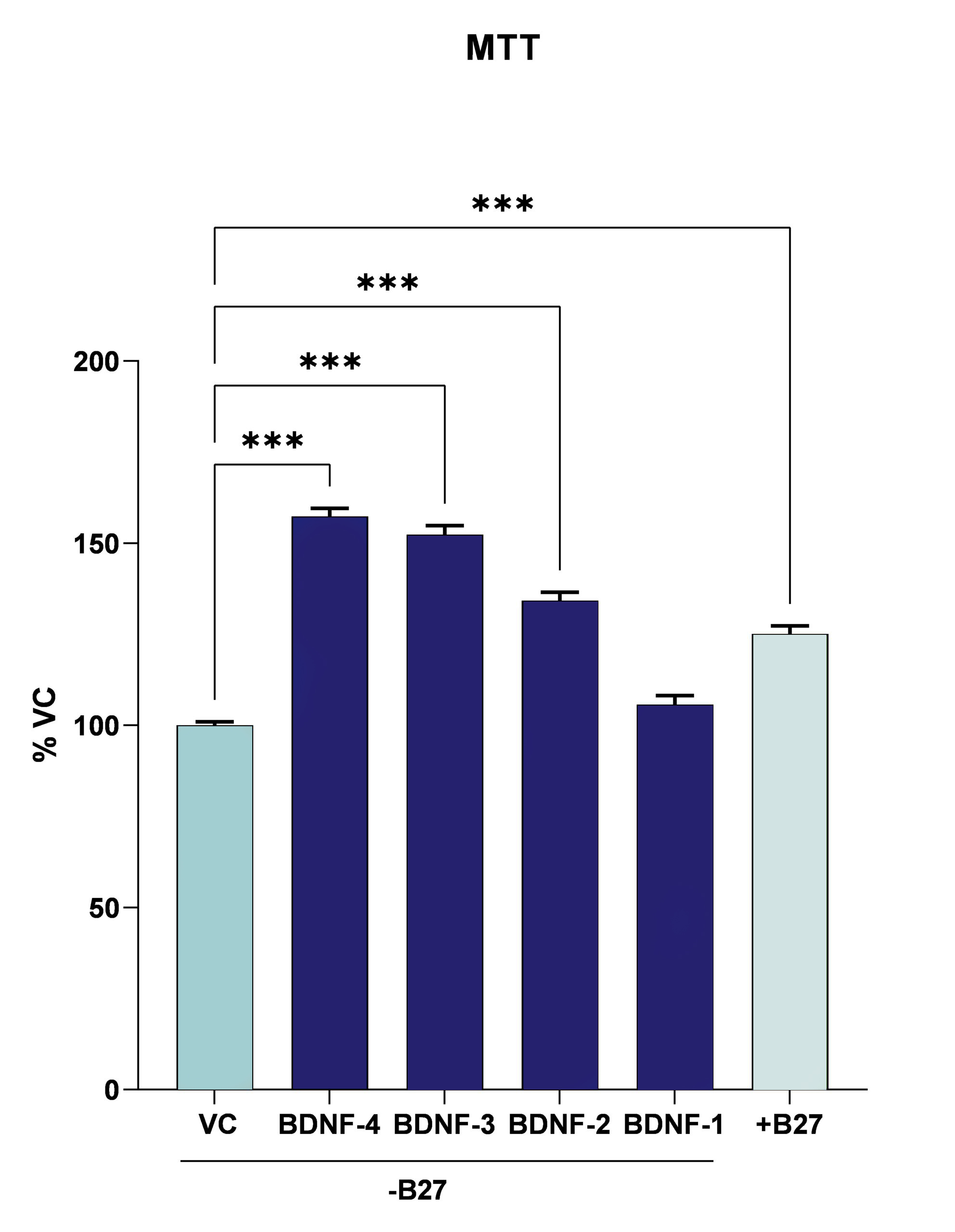
Figure 1: Metabolic activity assay (MTT) in murine cortical neurons upon withdrawal of B27. Data are displayed as group means (n=6) and represented as percent of the vehicle control. BDNF at the highest three concentrations (BDNF-2 to -4) significantly increases viability of the cells. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet’s post hoc test. ***P<0.001.
The effect of growth factor withdrawal on apoptosis (Fig.2A) and necrosis (Fig.2B) can be evaluated by the YO-PRO™-1 Iodide assay. Analysis of murine cortical neurons shows that the effect can be reversed by BDNF treatment (Fig. 2).
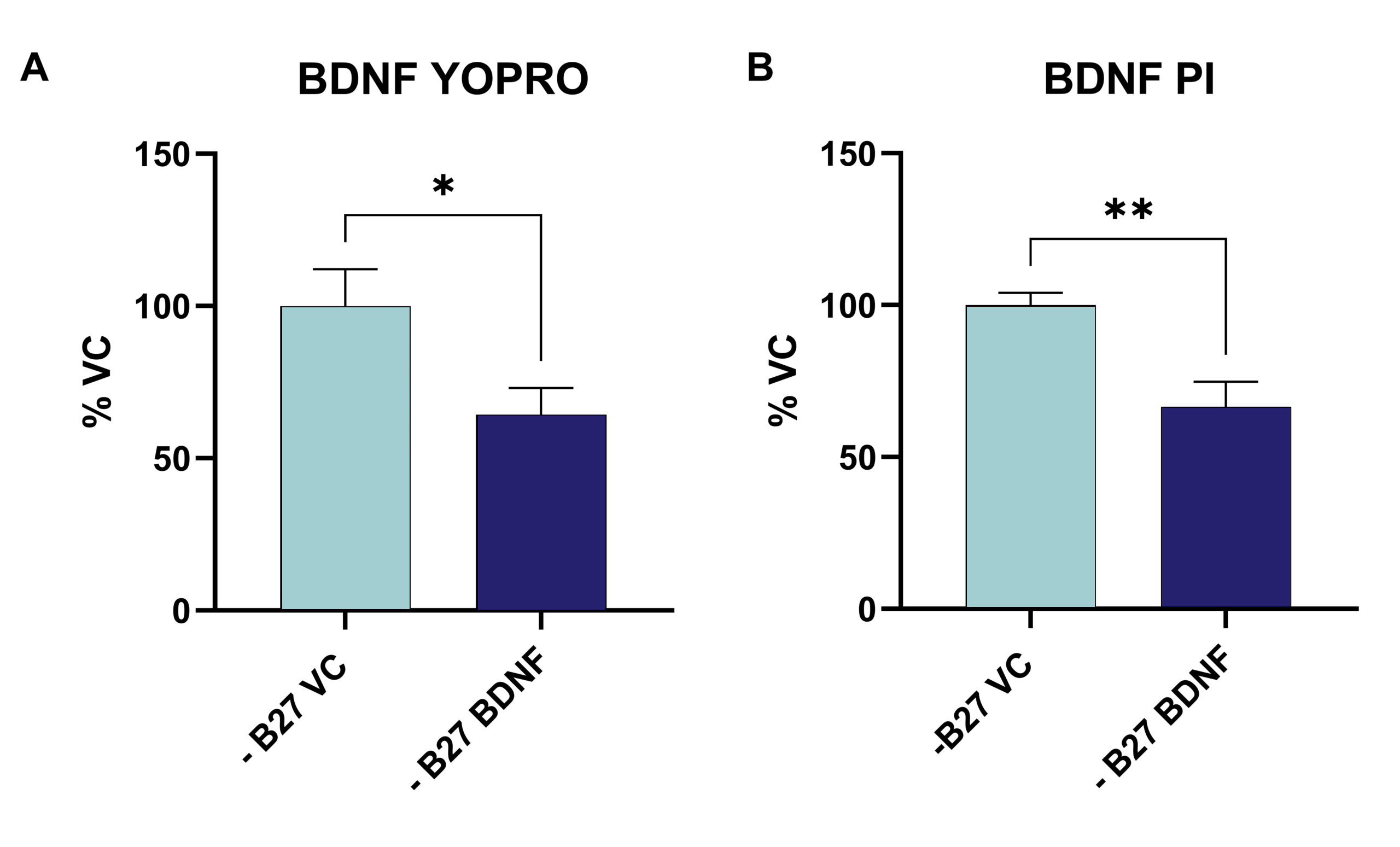
Figure 2: YO-PRO™-1 Iodide assay to detect apoptotic cells (A) in combination with PI staining for necrotic cells (B). Data are displayed as group means (n=5) and represented as percent of the vehicle control. BDNF significantly reduces the amount of necrotic and apoptotic cells after B27 removal. Unpaired t-test: *p<0.05 **P<0.01.
Furthermore, B27 withdrawal induced apoptosis can be monitored in live cells using the Incucyte® live-cell imaging system.
Contact Scantox to discuss the setup of your next experiments.
