Cuprizone-Induced Multiple Sclerosis
Cuprizone is a copper chelator, that causes rapid demyelination and gliosis, as well as rapid proliferation of glia subtypes. The cuprizone mouse model captures several aspects of multiple sclerosis (MS).
The most important characteristics of cuprizone-treated mice are:
- Astrocytosis
- Reduced MAO activity
- Motor deficits
The cuprizone-induced mouse is the most frequently used model among the toxin-induced MS models and is used to study mechanisms of de- and re-myelination, gliosis as well as motor deficits. This mouse model is thus suitable to assess certain aspects of the MS pathology and to test new compounds for the treatment of MS.
C57Bl/6 mice are fed with cuprizone chow for 1 month. Behavioral changes can be assessed within the last week of cuprizone treatment. Cuprizone-induced mice show a reduced motor performance in the beam walk test (Figure 1A), a decreased monoamine oxidase activity in the brain (Figure 1B), as well as increased hippocampal astrocytosis (Figure 1C).
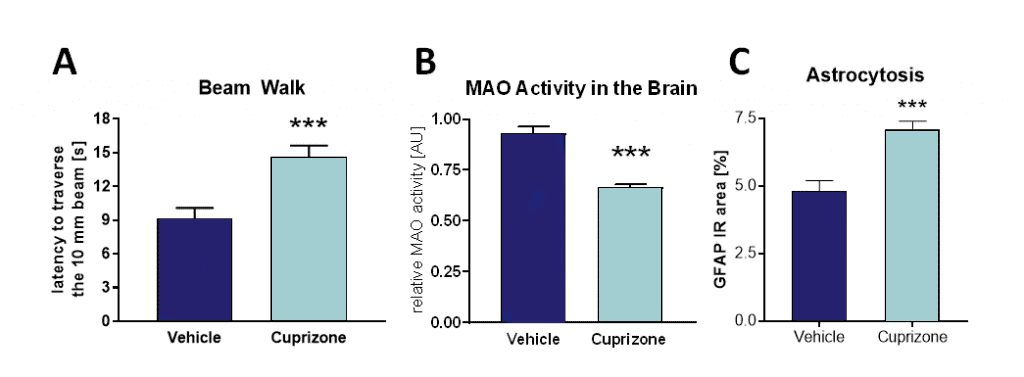
Figure 1: Beam walk test, MAO activity and astrocytosis of C57BL/6 mice after 4 weeks of cuprizone treatment. A: Latency to traverse a 10 mm wide square beam in seconds. B: MAO activity in brain lysates. C: Astrocytosis in the hippocampus by GFAP labeling. Mean + SEM; n = 10 per group; unpaired t-test/Mann Whitney test; ***p<0.001.
EAE-Induced Multiple Sclerosis
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) shows many pathological similarities to multiple sclerosis (MS) and is therefore often used as model to mimic MS by injecting myelin-oligodendrocyte-glycoprotein (MOG) in combination with pertussis toxin (PTX).
The most important characteristics of EAE-treated mice are:
- Clinical signs
- Reduced muscle strength
- Neurodegeneration
- De-myelination
C57Bl/6 mice are injected with MOG and PTX and monitored for 5 weeks. Motor performance and spinal cord neuropathology can be evaluated after completion of the treatment (Figure 2). EAE treatment causes an increase in clinical signs (Figure 2A), a decrease in muscle strength (Figure 2B), an increase in plasma neurofilament-light chain (NF-L) levels (Figure 2C), and an increase in demyelination (Figure 2D). Additional treatment with Fingolimod (Fingo) improves clinical signs (Figure 2A) and reduces plasma NF-L levels (Figure 2C).
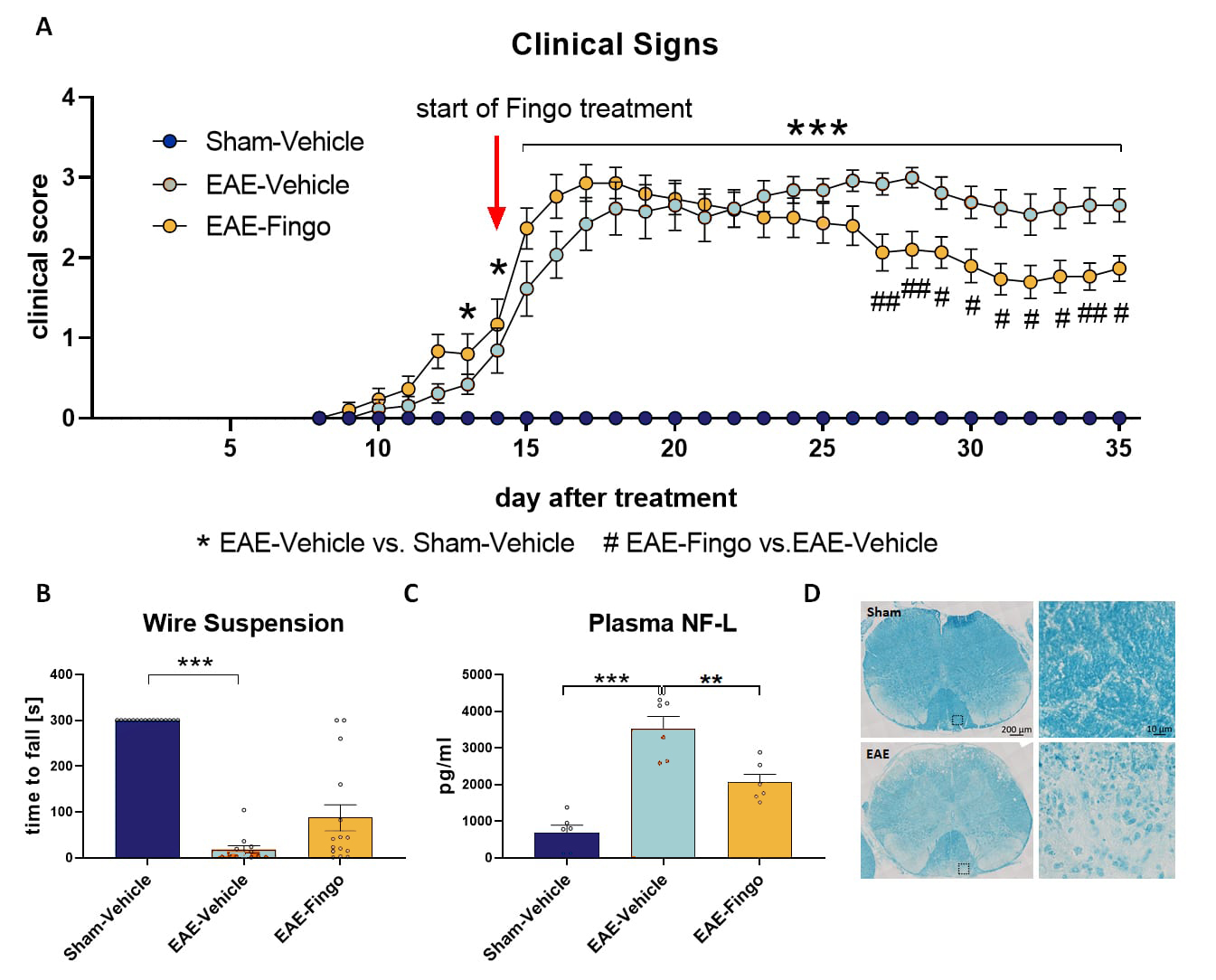
Figure 2: Clinical signs, motor deficits, neurofilament-light chain levels and demyelination of EAE-treated mice. EAE-treated C57Bl/6 mice were tested for clinical signs (A), muscle strength in the wire suspension test (B), plasma neurofilament-light chain (NF-L) levels and compared to vehicle-treated and EAE + Fingo treated mice (C). Luxol Fast Blue staining for myelin was performed in EAE- and Sham-treated mice (D). A-C: n = 13 16 per group; Mean + SEM; Kruskal-Wallis One-way ANOVA followed by Dunn‘s multiple comparisons post hoc test; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. *EAE-Vehicle vs. Sham-Vehicle; #EAE-Fingo vs. EAE Vehicle. Fingo = Fingolimod.
Scantox offers a custom-tailored study design for both induced MS models, and we are flexible to accommodate your special interest. We are also happy to advise you and propose study designs. Our induced models show a relevant multiple sclerosis (MS) phenotype shortly after treatment. This grants a remarkable fast processing time of your MS study. Furthermore, sham/vehicle-treated wild type mice can serve as control needed for proper study design.
We are happy to evaluate the efficacy of your compound in our induced MS mouse models! The most common readouts depend on the model and include:
